PC (personal computer), the term personal computer originated from IBM's first desktop computer model in 1981, prior to the Apple II personal computer.
A personal computer consists of a hardware system and a software system. It is a device that can run independently and perform specific functions.
Hardware system: refers to the physical equipment of the computer such as power supply, motherboard, CPU, memory, hard disk, etc.
l Software system: refers to a program designed to facilitate the use of a computer. The software system includes system software and application software. System software refers to programs that are primarily used to control and manage computer resources, such as operating systems, compilation systems, and so on. Application software refers to various programs that can run in the operating system, such as game software, work software, and so on.
Personal computers do not need to share the processing of other computers, resources such as disks and printers can work independently. From desktops (or desktops, desktops), laptops to netbooks and tablets, and ultrabooks are all personal computers.
With the popularity of smartphones and tablets, most people may already prefer the kind of office entertainment that can be done with their fingers. Recently, both domestically and abroad, there are many "experts" who believe that in the near future, traditional PCs will be replaced by more portable mobile phones and tablets.
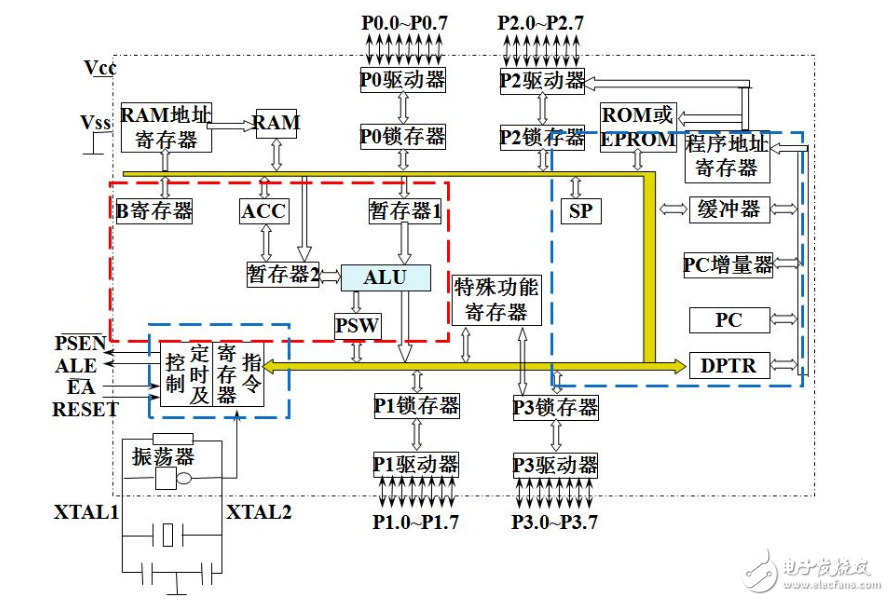
DPTR is a special function register in some microcontrollers. It is a 16-bit special function register. Its high byte register is represented by DPH, the low byte register is represented by DPL, and DPTR can be handled as a 16-bit register. It can also be used as two independent 8-bit registers.
The main function is to store a 16-bit address. As an address register for in-chip RAM addressing (indirect addressing), it is called a data pointer. It can also transfer the contents of the address in the external RAM to the contents pointed to by the address of the internal RAM. The addresses of DPH and DPL are 83H and 82H, respectively.
The difference between PC and DPTRThe PC is the program counter. Does not belong to the special function register. It stores the address of the 16-bit memory location of the next instruction to be fetched. When one byte is fetched, the value of the PC is automatically added to prepare for the next instruction.
Another point: After the microcontroller is reset, the PC is automatically cleared. The PC value is not incremented when the interrupt program is executed.
Which of the special function registers of the 51 MCU are 16 bits?
DPTR, because the 51 MCU is an 8-bit machine, but the address bus is 16 bits, so the data pointer must be 16 bits, and the count registers of the two timers are also 16 bits. These three 16-bit registers are You can operate on the upper and lower 8 bits of each other. Since you want to learn the single-chip microcomputer, you must learn the basics of the single-chip microcomputer. If you want to study the book well, you can understand it.
Rn is the working register group. At the same time, only one group is running, which one is running, there is PSW (the status register determines - you can set it yourself). The special function register includes 21, among which there are P0, P1, P2, P3 (store I /O data), PSW (status register), ACC (accumulator), B (multiply register), SP (stack pointer), DPL (DPTR low), DPH (DPTR high), PCON (power control, baud rate selection ), TCON, TMOD, TL0, TH0, TL1, TH1 (timer interrupt parameter), IE (interrupt setting), IP (interrupt priority), SCON (serial interrupt), SBUF (serial buffer) {visible program counter PC Not a special function register}
The difference between PC and DPTR in 51 single chip microcomputer
The MCS51 instruction system interacts with the external program memory as two table lookup instructions (MOVC), and its addressing mode uses the indirect addressing mode of the base address offset. 1.MOVC A, @A+DPTR2.MOVC A, @A+ PC 1 is a remote table lookup instruction 64KB 2 is a short-range table lookup instruction 256BPC is a program counter, used to place the next instruction address to be executed, is a 16-bit special register, the addressable range is 0-65536 64K, PC It is physically independent of SFR. The DPTR is a SFR. The PC pointer is a pointer to the instruction address: 0001H, 0002H, 0003H. . .
The current value of pc is the base address (refers to the first address of this instruction), single-byte instruction. When executed, pc+1 points to the address of the next instruction, and then adds the content of accumulator a to form a change. Address addressed address movc a, @a+pc (pc) "----(pc)+1, (a) "----((a)+(pc)
Using dptr as the base register, add the contents of dptr and the contents of accumulator a to get the index address.
Movc a, @a+dptr (a) "-----((a)+(dptr))
The indexed addressing mode is dedicated to program memory access and cannot access data memory. When using indexed addressing, assign a value to a and dptr to determine the address. When using pc as the base address, you only need to assign a value.
MOVC A, @A+DPTR MOCX A, @A+PC What is the difference between these two commands?
Both are look-up tables, the difference between the former can be up to 64K, the latter can only check the 256-byte address range
DPTR is a 16-bit register, because it is 16 bits, so its range is 0-0xffff is the range of 0-64K. Then it can be used to indirectly address access to internal or external memory (whether it is program memory or data storage.). The PC is the program counter and is also a 16-bit counter. Every one machine cycle, the PC will add one. The contents of it store the address currently stored in the CPU in the ROM, so MOVC A, @A+PC is not the same when the program is executed at different times.
DPTR is a data pointer, PC is the program counter instruction MOVC A, @A+DPTR means: the value of DPTR is added to the value of ACC, and the data of the program memory address indicated by the result is sent to ACC. This command has nothing to do with the current PC (program counter) value. For example, if DPTR=0300H (this value is given by itself) before execution, ACC=18H, [0318H]=0ABH, then ACC=0ABH, DPTR after execution. The same, MOVC A, @A+PC means: the value of the PC (program counter) is added to the value of ACC, and the data of the program memory address pointed to by the result is sent to the ACC, which is independent of the DPTR. The PC (program counter) value differs depending on the location of the instruction, so the execution result of the instruction is different at different positions of the program. The rest of the same instruction
Liquid Crystal Display For Home Appliances
Liquid Crystal Display For Home Appliances,High Resolution Portable Lcd Display,Refrigerator Lcd Liquid Crystal Display,Response Fast Remote Lcd Monitor
Dongguan Yijia Optoelectronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.everbestlcdlcms.com